What Is a Water Softener and How Does It Work?

What Is a Water Softener and How Does It Work?
If you're a homeowner, you're likely familiar with the frustrating challenges of hard water. It can damage your appliances, leave a film of soap scum all over your bathroom and kitchen, and even dry out your hair and skin. But did you know that a water softener can help?
Removing the minerals that cause water hardness can save you from replacing ruined water heaters and faucet heads and from spending hours cleaning up soapy residue. And with over 85% of the United States relying on hard water, investing in a water softener can save you time, energy, and money while protecting your home and property.
What is a Water Softener?
A water softener is an appliance used to address the hard water problem. Hard water contains high levels of minerals (calcium and magnesium), which can cause various issues in a household. These minerals can clog plumbing, create scale on fixtures, and damage hot water appliances like water heaters and dishwashers.
Components Of Water Softener
The primary components of a water softener include the control valve, brine tank, and mineral tank.
- The control valve regulates the water softener's regeneration cycle based on water usage.
- The brine tank holds salt, which is used during the regeneration process.
- The mineral tank contains a resin that is responsible for the ion exchange process.
How a Water Softener Works
A water softener works on a principle called ion exchange. The process involves removing hardness minerals from the water and replacing them with sodium ions. Here's a step-by-step explanation of how a water softener works:
- Raw water enters the water softener tank from the home's main water line.
- Inside the tank, there are ion exchange resin beads. These beads are responsible for removing the hard minerals from the water.
- An exchange or swap occurs as the water flows through the resin bed. The minerals such as calcium and magnesium ions in the water are more likely attracted to the resin beads. And sodium ions from the resin beads are emitted into the water, softening water.
- The water softener also includes a brine tank where salt is stored. The salt is typically in the form of pellets.
- The system periodically initiates a regeneration cycle when it requires recharging. This is typically based on a schedule or determined by the hardness level of the water and the water usage in the home.
- During the regeneration cycle, the brine tank fills with water, dissolving the salt and creating a salt solution or brine.
- The brine solution is drawn into the water softener system, and a backwash occurs. Raw water enters the system and agitates the resin bed, removing any debris or sediment that may have accumulated.
- The salt solution passes over the resin bed, and the sodium ions from the resin beads replace the hardness minerals captured by the resin. This helps regenerate the resin bed, making it ready to remove hardness minerals again.
- A final rinse cycle is performed to flush out any remaining salt from the system.
- Once the regeneration cycle is complete, the water softener returns to its service position. The treated and softened water is then distributed throughout the home for use.
Note that a significant amount of water may be used during the regeneration process, and some water with brine content will be drained. In addition, the regeneration frequency depends on factors like water hardness and household water consumption.
Different types of water softeners may have variations in their design, but the basic principle of ion exchange remains the same. For example, some all-in-one systems may integrate the brine tank into the outer casing while the main softener tank contains resin beads.
Overall, a water softener helps remove hardness minerals from water, improving the water quality and reducing issues related to hard water, such as scale buildup on fixtures and appliances.
Is Soft Water Safe To Drink?
This question comes to many people's minds: is soft water safe to drink? The answer is generally yes. Soft water is water with reduced mineral content, typically through ion exchange. While some people favor the taste of hard water, soft water is generally considered safe and healthy to drink.
Some people find soft water easier on their digestive system and may help prevent specific health problems. But, of course, it's always a good idea to consult with your physician if you need any help with the safety of your drinking water.
How to Tell If You Need a Water Softener
Suppose you are experiencing the uncomfortable effects of hard water in your home, such as lackluster showers and baths with minimal soapy lather and soap scum residue (skin and hair). In that case, a water softener may benefit you. Hard water can also affect your laundry, making it look dull, dingy, and stiff. Cleaning becomes more challenging due to scale buildup on shower doors and sinks, and your dishes may have spots and a thin filmy residue after washing. In addition, the excess scale on your water-consuming appliances and fixtures can shorten their lifespan.
A water softener can help address these issues by removing the hard minerals (calcium & Magnesium) from your water, making it more satisfying to bathe without noticeable soap scum residue. It can also save your favorite clothes by providing brighter, softer, cleaner laundry with reduced scale buildup. Moreover, with a water softener, you may experience better performance from your plumbing fixtures, pipes, and water-consuming appliances like the dishwasher, coffee maker, and humidifier.
Aqua Hygiene Water softener Whole House System
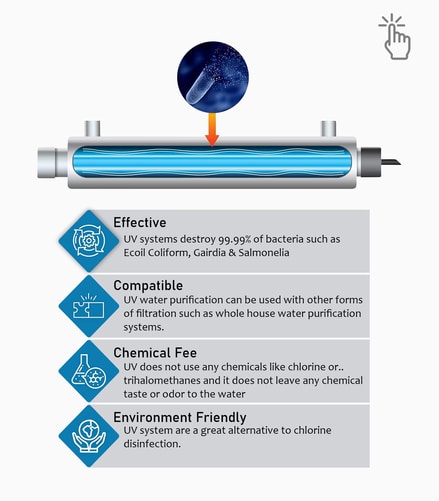
UV Disinfection system - Whole House water softener system
Whole House Water Softener system
NO MORE HARD WATER. NO MORE PROBLEMS.
Aqua Hygiene water softener system is tested to prevent and remove the damage done by hard water. Extending the life of washing machines, water heaters, and other appliances. And getting cleaner and better-smelling laundry, soft water also keeps your skin and hair healthy

Alternatives to water softeners
You may wonder about your options if you live in a municipality where water softeners are banned. While alternatives are available, they may provide different benefits than a water softener.
- Whole house multimedia water filter systems, for example, use another method to prevent scale buildup, but they do not remove hardness minerals from water. This can lead to issues with laundry, dishes, and soap scum.
- Reverse osmosis filters technically soften water, but they are not a suitable choice since they are not designed to handle hard water. If you are still determining which option is best, consider consulting with a professional to find the right solution.
Final Verdict:
Finally, investing in a water softener can save homeowners time, energy, and money while protecting their homes and property. By removing the minerals (calcium & Magnesium) that cause water hardness, a whole house water softener can prevent appliance damage and reduce the time spent cleaning up soapy residue. While water softener has some disadvantages, such as increased sodium content and environmental impact, the benefits generally outweigh the drawbacks. If you are experiencing the uncomfortable consequences of hard water in your house, a water softener may be your solution. Consider consulting with a professional to find the right option for you.